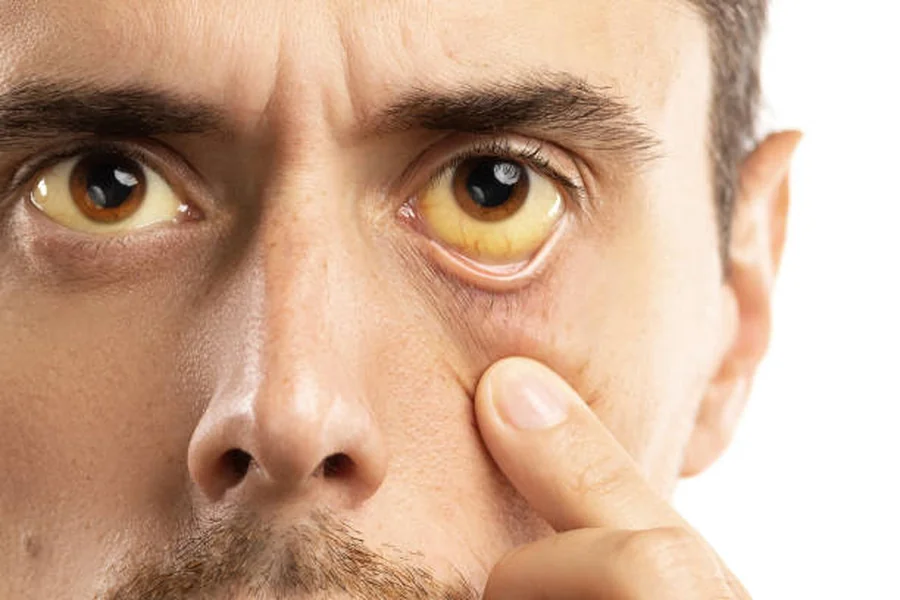
Jaundice is a medical condition marked by a yellowing of the skin and eyes, caused by elevated bilirubin levels in the bloodstream. This often occurs when liver function is impaired, preventing efficient processing and elimination of bilirubin. The condition can affect individuals of all ages, from newborns to adults, and may signal underlying liver or bile duct issues.
In Singapore, jaundice remains a common health concern, particularly among infants, while adults may experience the condition due to liver disease, infections, or medication side effects. The nation’s healthcare system has advanced significantly, employing innovative medical technologies and research-driven approaches. Collaborative efforts between public institutions and private healthcare providers have improved treatment quality, allowing patients to receive timely and effective care.
This article presents an in-depth overview of jaundice, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest developments in Singapore’s healthcare system.
Understanding Jaundice
Causes of Jaundice
Jaundice arises from the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood. Contributing factors may include liver disease such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, obstruction of bile ducts, hemolytic anemia, or reactions to certain medications. These factors interfere with bilirubin metabolism and excretion, leading to the characteristic yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Symptoms Associated with Jaundice
Individuals with jaundice typically exhibit yellowed skin and eyes, darkened urine, and pale stools. Additional symptoms can include fatigue, abdominal discomfort, itching, nausea, and mild fever. Recognizing these indicators early allows for prompt evaluation and management.
Potential Risks if Untreated
Leaving jaundice untreated can result in severe complications, including worsening liver disease, infection, or long-term health issues. Prompt medical attention reduces the likelihood of these outcomes and contributes to improved quality of life and reduced healthcare burdens.
Diagnosis of Jaundice in Singapore
Standard Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosis generally begins with a clinical assessment and blood tests to measure bilirubin levels and evaluate liver function. Imaging techniques, including ultrasound and CT scans, may be used to detect structural abnormalities or obstructions in the liver and bile ducts. These steps allow medical teams to identify underlying causes accurately and plan appropriate interventions.
Advancements in Detection
Recent innovations in diagnostics have introduced non-invasive bilirubin monitors and portable testing devices. Some facilities in jaundice treatment Singapore are integrating machine learning systems to analyze blood test results efficiently, enabling quicker detection and more precise care.
Quality of Diagnostic Services
Singapore’s healthcare system provides high-standard diagnostic services, supported by advanced technology and skilled medical professionals. Stringent regulations and continuous improvements contribute to accurate diagnoses, reliable patient care, and faster access to treatment.
Jaundice Treatment Approaches in Singapore
Standard Treatment Methods
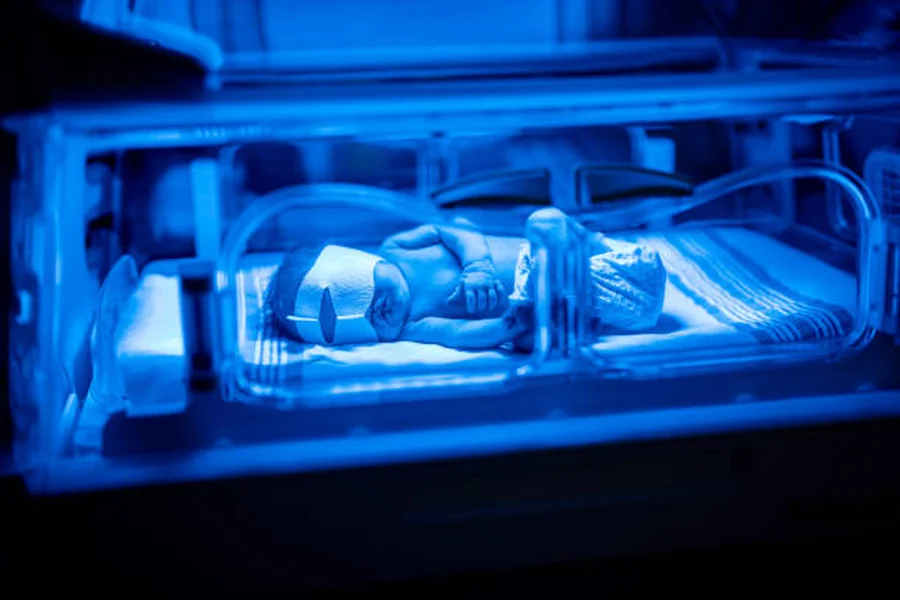
Treatment targets the underlying cause of jaundice. For newborns, phototherapy is commonly used to reduce bilirubin levels safely. Adults may receive medications to manage infections, inflammation, or liver dysfunction. In severe cases, interventions like liver transplantation may be necessary.
Treatment Process Overview
Care usually involves multiple stages: evaluation, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and monitoring. Each step is guided by specialists to address individual health needs, adjust therapies as required, and track recovery progress.
Challenges During Treatment
Patients undergoing treatment may experience emotional stress, physical side effects, and financial pressures. Managing these factors is important for maintaining adherence to care plans and supporting overall well-being throughout recovery.
Breakthroughs in Singaporean Jaundice Care
Innovative Technologies
Medical devices like non-invasive bilirubin meters and modern phototherapy systems have improved treatment effectiveness and patient comfort. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring, allowing adjustments to therapy without invasive procedures.
Successful Treatment Methods
Singapore has integrated advanced techniques, including targeted medications for liver conditions and improved neonatal care protocols. These methods contribute to higher recovery rates and set benchmarks for regional healthcare excellence.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Doctors, nurses, and medical researchers contribute by refining diagnostic protocols, researching new therapies, and implementing patient-centered care strategies. Their expertise helps maintain treatment quality, reduces complications, and supports positive outcomes.
Case Studies of Jaundice Treatment
Examination of Real Cases
Anonymous case studies highlight the treatment of patients across age groups. Each scenario demonstrates the practical application of diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
Treatment Approaches Followed
Patients underwent structured care involving assessment, personalized treatment planning, and continuous evaluation. Interventions included phototherapy, medication management, and monitoring for complications.
Outcomes and Recovery
Recovery rates varied based on age, overall health, and underlying conditions. Many patients experienced significant improvement with timely and appropriate care, reinforcing the importance of specialized treatment strategies.
Future Trends in Jaundice Care
Emerging technologies, including AI-assisted diagnostics and advanced phototherapy, are improving treatment precision. Telemedicine platforms are expected to provide greater access to expert consultations, while ongoing research may yield new pharmaceuticals targeting bilirubin metabolism or liver regeneration.
These developments aim to refine treatment approaches, reduce recovery times, and improve patient comfort and safety. Continued research contributes to earlier detection, more efficient therapies, and broader accessibility across the healthcare system.
Conclusion
Jaundice is a manageable condition when identified early and treated appropriately. Singapore offers advanced medical services, skilled professionals, and innovative technologies to diagnose and manage jaundice effectively. Through a structured treatment process, patients can recover safely while minimizing complications. Emerging technologies and continued research promise further improvements, making Singapore a trusted destination for effective jaundice care. Patients benefit from tailored interventions, continuous monitoring, and professional guidance, ensuring better health outcomes and sustained well-being.